The Quantian Scientific Computing Environment
A Knoppix / Debian variant tailored to numerical and quantitative analysis.
Executive Summary: The most recent version is 0.7.9.2 dated 26 February 2006 and released March 1, 2006 --- the second Quantian version based on the new Knoppix 4.0.2 release. The (compressed) iso file is now 2.7 gb and corresponds to about 7.6 gb of software -- all configured and ready to be booted and used.
Support for openMosix has been backported from clusterKnoppix v3.6 with the reliable openMosix-enabled 2.4.27 kernel. The packages list ordered by size and the detailed packages list provide details about the included programs, see the changelog for a detailed summary of all the changes. Download informations are provided below. Also see the Quantian blog page, the changelog, the todo and bugs pages, and well as the set of short howtos for detailed information.
What is Quantian?
Quantian is a remastering of Knoppix, the self-configuring and directly bootable cdrom/dvd that turns any pc or laptop (provided it can boot from cdrom/dvd) into a full-featured Linux workstation. Quantian also incorporates clusterKnoppix and adds support for openMosix, including remote booting of light clients in an openMosix terminal server context. Earlier releases are still available; see below for URLs for downloads as well as ordering information.Brief introductory information is available in a recent paper published in The Political Methodologist, slides from presentations at UseR! 2006 (June 2006), DSC 2005 (August 2005), Usenix 2004 (July 2004), and in the earlier (revised) paper about Quantian that has appeared in the DSC 2003 Proceedings.
Quantian is an extension of Knoppix and clusterKnoppix from which it takes its base system of around gigabytes of software, along with fully automatic hardware detection and configuration. To this, it add about five gigabytes of software.
What does Quantian contain?
Quantian differs from Knoppix by adding a large number of programs of interest to applied or theoretical workers in quantitative or data-driven fields. The added quantitative, numerical or scientific programs comprise- R, including essentially all packages from CRAN (excluding only non-Unix packages such as MimR, or ROracle which needs special headers and libraries) and BioConductor; the snapshot was made February 25, 2006) as well as some from other R package repositories, out-of-the box support for the powerful ESS modes for XEmacs, the Ggobi visualisation program, the Rpy RPy Python interface, the RSPerl bi-directional integration with Perl, the award-winnning JGR Java GUI for R, the Rserve headless R server, the Rpad interactive web interface and initial support for the RKward gui for R.
- bioinformatics tools such all packages from the BioConductor project, as well as bioperl, biopython and applications such as blast2, clustalw, ImageJ, and hmmer;
- Octave, with add-on packages octave-forge, octave-sp, octave-epstk, matwrap and Inline::Octave as well as other matrix language environments;
- Computer-algebra systems Maxima (including the X11 front-end and emacs support), Pari/GP, GAP, GiNaC, YaCaS, Axiom, Mathomatic and Calc;
- GSL, the Gnu Scientific Library (GSL) including example binaries;
- the QuantLib quantitative finance library including its Python interface;
- the Grass geographic information system;
- the OpenDX and Mayavi data visualisation systems;
- TeXmacs for wysiwyg scientific editing as well as LyX and kile for wysiwyg (La)TeX editing;
- various Python modules including Scientific and Numeric Python;
- Cernlib, a large number of programs and libraries from the CERN particle physic lab;
- the bochs, wine and qemu emulators;
- office suites such as OpenOffice.org and KOffice as well as Abiword, Gnumeric and the Gimp;
- and various other programs such as apcalc, aplus, aribas, autoclass, DrGeo, euler, evolver, freefem, ftnchek, gambit, geg, geomview, ghemical, glpk, gnuplot, gperiodic, gri, gmt, gretl, ImageMagick, IPE, lam, lp-solve, mcl, mpich, mpqc, multimix, rasmol, plotutils, pgapack, pspp, pdl, rcalc, SQLite, Tclsh, yorick, xaos, and xppaut;
At the same time, all the distinguishing features that set Knoppix apart are retained in Quantian:
- Auto-configuration of graphics, sound, disks, networking, auxiliary devices which is second to none among computer installations
- A recent version (actually mostly 3.5 with some 3.4) of the KDE desktop environment
- The GNU compiler suite comprising gcc, g77, g++ compilers including gcj
- Perl and Python with loads of add-ons, plus other languages such ruby, tcl, Lua...
- The Emacs and Vim editors, as well as kate, jed, joe, nedit and zile
- Gnumeric, Koffice, ... office tools, with OpenOffice.org added back in
- A Swiss-army knife collection of networking tools allowing access to wired and wireless lans, covering ethernet, isdn or dial-up modems
- And still in Quantian though no longer in Knoppix: a complete teTeX TeX / LaTeX setup for scientific publishing along with wysiwyg frontends such as kile and LyX / LyX-Qt, the preview mode for emacs editors, several additonal bibtex tools, and other goodies such as prosper, pdfscreen and beamer for presentations as well as numerous Bibtex utilities.
Last but not least, and thanks to clusterKnoppix, quantian allows to build openMosix clusters in a matter of minutes -- and to immediately use them thanks to the 5 gb of added scientific software.
Screenshots
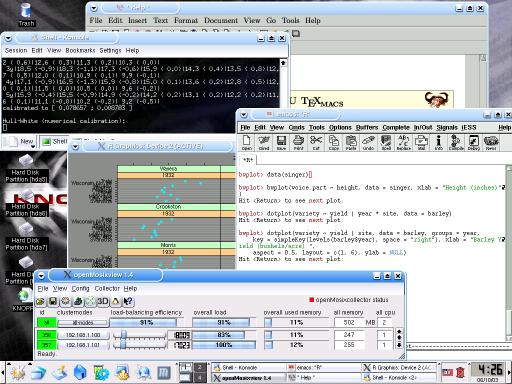
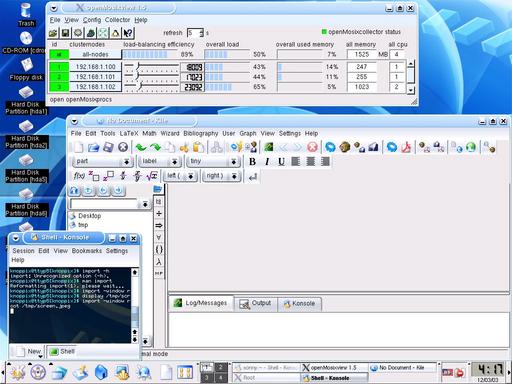
You can click on any of the images to see a full-size chart. The first screenshot shows version 0.3 with openMosix running on a cluster with two computers, an R session (run from with XEmacs using the ESS mode) with lattice graphics, the QuantLib demo 'BermudanSwaption' as well as TeXmacs -- and the Knoppix 3.2 heritage is clearly visible on the background.The second screenshot shows Quantian version 0.4.9.3 with an openmosixview display of a three-node / four-cpu cluster as well as the kile LaTeX frontend -- and the Knoppix 3.3 background image.
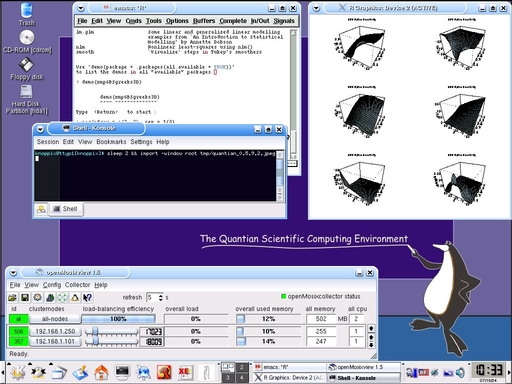
The third screenshot shows Quantian 0.5.9.2 with its new custom background which was contributed by Ed Pegg, Jr. Also shown are an R session running in an XEmacs buffer controlled by ESS. The R session displays a demo from Rmetrisc which displays the sensitivities of financial options to various parameters--the so-called 'greeks'--in a 3x2 display. Also shown is openMosixview.
Mailing lists
Two mailing lists exist for Quantian, courtesy of Debian's Alioth host:- quantian-announce for announcements only, very low volume, posting restricted to the listowner/maintainer
- quantian-general for general discussions about Quantian, posting restricted to subscribers -- so please subscribe before posting
Downloads
Two primary machines exist with Quantian archives:- The main archive is on the US West Coast is the Quantian archive at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle (which replaces for U of Washington mirror), and
- the backup archive on the US East Coast on Greg Warnes' machine at Yale.
Note that the increased filesize may create problems with web-caching software that can only handle files of up to 2 gb in size. It may be safer to use rsync or bittorrent instead of http webdownloads.
European mirrors site are available in Madrid, Spain at RedIRIS (also with ftp access) and Aachen, Germany at RWTH (also with ftp access).
Rsync access is available at the Fred Hutchinson archive.
rsync rsync://quantian.fhcrc.org/quantian/would retrieve a directory listing, and for example
rsync -v rsync://quantian.fhcrc.org/quantian/boot_0.6.9.x.iso .would (verbosely) retrieve the 0.6.9.x-compatible boot image to the current directory.
Bittorrent A new torrent is available thanks to the Linux Mirror Project, as well as at EpiGenomics (in Germany). U of Washington used to have both a bittorrent seeder and mirror with a nice graphical summary of usage, but that machine is currently, and for the foreseeable near-term future, unavailable.
Quantian for purchase
Quantian dvds and cdrom are available pre-made from the following third-party resellers:- BudgetLinuxCDs.com has the dvd for $7.50 for the cdrom for $2.50.
- CheapBytes.com has the dvd for $11.99, and cdroms from for $4.99 plus shipping.
- Frozentech.com has the most recent dvd at $1.99 with $0.49 shipping.
- LinCD.com offers the dvd for $2.99, and an older cdrom release for $1.99.
- LinuxCentral.com lists 0.7.9.2 for $9.95.
- ulnx.com has older Quantian cdroms for $2.29 plus shipping.
- In Australia, lankum.com offers Quantian cdroms for A$5.5 and dvds for A$9.9.
- In Germany, BSDISO offers Quantian cdroms premade for EUR 3.95 plus EUR 2 for shipping.