#43: r2u Faster Than the Alternatives
Welcome to the 43th post in the $R^4 series.
And with that, a good laugh. When I set up Sunday’s post, I was excited enough about the (indeed exciting !!) topic of r2u via browser or vscode that I mistakenly labeled it as the 41th post. And overlooked the existing 41th post from July! So it really is as if Douglas Adams, Arthur Dent, and, for good measure, Dirk Gently, looked over my shoulder and declared there shall not be a 42th post!! So now we have two 41th post: Sunday’s and July’s.
Back the current topic, which is of course r2u. Earlier this week we had a failure in (an R based) CI run (using a default action which I had not set up). A package was newer in source than binary, so a build from source was attempted. And of course failed as it was a package needing a system dependency to build. Which the default action did not install.
I am familiar with the problem via my general use of r2u (or my r-ci which uses it under the hood). And there we use a bspm variable to prefer binary over possibly newer source. So I was curious how one would address this with the default actions. It so happens that the same morning I spotted a StackOverflow question on the same topic, where the original poster had suffered the exact same issue!
I offered my approach (via r2u) as a comment and was later notified of a follow-up answer by the OP. Turns our there is a new, more powerful action that does all this, potentially flipping to a newer version and building it, all while using a cache.
Now I was curious, and in the evening cloned the repo to study the new approach and compare the new action to what r2u offers. In particular, I was curious if a use of caches would be benficial on repeated runs. A screenshot of the resulting Actions and their times follows.
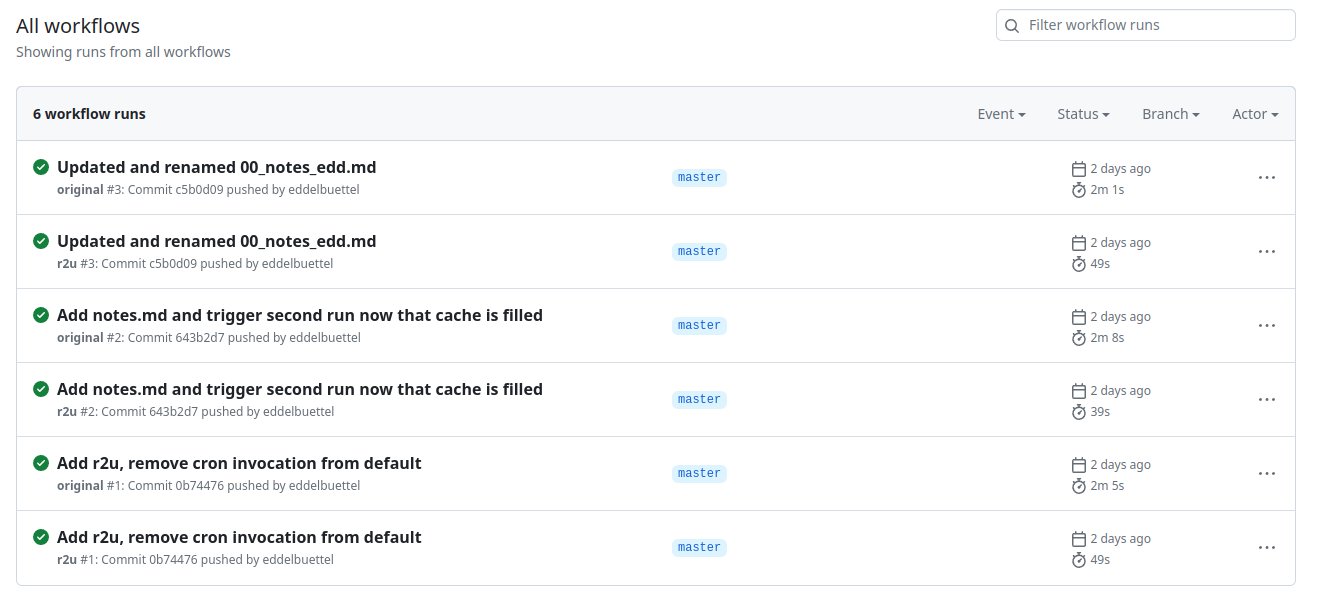
Turns out maybe not so much (yet ?). As the actions page of my cloned ‘comparison repo’ shows in this screenshot, r2u is consistently faster at always below one minute compared to new entrant at always over two minutes. (I should clarify that the original actions sets up dependencies, then scrapes, and commits. I am timing only the setup of dependencies here.)
We can also extract the six datapoints and quickly visualize them.
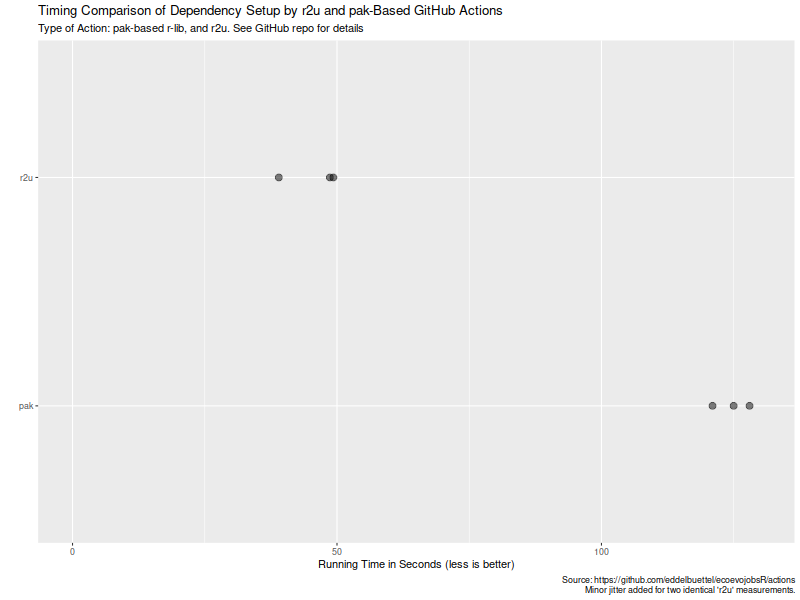
Now, this is of course entirely possibly that not all possible venues for speedups were exploited in how the action setup was setup. If so, please file an issue at the repo and I will try to update accordingly. But for now it seems that a default of setup r2u is easily more than twice as fast as an otherwise very compelling alternative (with arguably much broader scope). However, where r2u choses to play, on the increasingly common, popular and powerful Ubuntu LTS setup, it clearly continues to run circles around alternate approaches. So the saying remains:
r2u: fast, easy, reliable.
If you like this or other open-source work I do, you can now sponsor me at GitHub.
This post by Dirk Eddelbuettel originated on his Thinking inside the box blog. Please report excessive re-aggregation in third-party for-profit settings.
Originally posted 2023-08-13, minimally edited 2023-08-15 which changed the timestamo and URL.